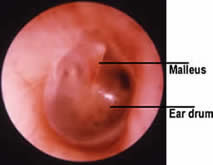
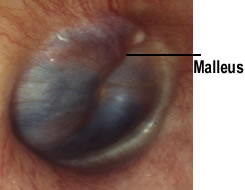
Glomus Tympanicum Symptoms Glomus tympanicum tumors develop inside the middle ear. The most common symptom is that of a pulsing sound as blood flows through the vessels of the tumor (pulsatile tinnitus). Other symptoms of a glomus tympanicum include a conductive hearing loss (caused by the tumor blocking sound transmission through the middle ear), ear pain and bleeding from the ear. Diagnosis Diagnosis is made based on the patient's symptoms, physical examination findings and a combination of tests. A common physical examination finding is that of a reddish/bluish mass behind the ear drum (tympanic membrane) (see Figures below). A hearing test and computed tomography scan (CT) are performed routinely. CT is needed to determine the size of a tumor and the relationships of the tumor with structures within the ear. CT tomography is also useful because it can see small erosions or openings in bone.
 |
 |
Normal Ear Drum
|
Glomus Tympanicum
|
Treatment The vast majority of glomus tympanicum tumors are treated with surgical removal. Small glomus tympanicum tumors are removed through incisions confined to the ear canal, while larger glomus tympanicum tumors are removed through an incision behind the ear. Surgical removal of glomus tympanicum tumors is typically performed under general anesthesia on an out patient basis (same day surgery). The chance of recurrence is quite low if the tumor is completely removed. |